Investigation Initialization, The Requirement Analysis
Investigation System Concepts
Based by a gap between systems objectives and condition in reality. To recognize the things which caused a failure to the system, then an analyst might better do the investigation in advance before conducting an action to improve the system.
Many reports in problem detection aren’t really trusted. They’re caused by :
• The systems objectives are too ideal so there’re possibilities that they could not be reached.
• Lack of resources and or attitudes.
• Systems measurement is less accurate.
• The systems objectives that was outdated.
• Differences between ideal system and the current system.
Some of the problem solving :
• Clarification of the system under way by investigating them in detail.
• Get the ideal system consensus.
• Develops some alternatives to lessen the gap between ideal systems with the systems under way.
• Choose the best alternatives.
To be noticed that the real objective of the investigation is to show the real problems that was happening, beside as a mode to an analyst to understand his system more clearly.
Constraints in investigation system
There are some constraint that might happened, those are :
• Time
Analysts often lacks time resources, so they may only done less investigation. Usually, time is related to the required expense problem.
• Cost
The released expense often related to the duration time for activity investigation, so that management will give the constraint of the expense.
• Knowledge
Manager of information system gives order to the junior analyst which not yet owned technical membership or the knowledge enough, so that will affect the investigation result less sharpen, or complete.
• Politics
Certain management, sides or possibly propagates the issues of the objectives to pursue activity of investigation.
• Interference
There are possibilities of the sides trying to interfere or arrange in one activity investigation so that will cause a bobber.
Recommendation
The result of the investigation is a recommendation that contains :
• Not taking any action because there’re no problems discovered.
• Doing regular system maintenance for minor problems.
• Improving the ability and skill of the user in using information system.
• Reconsider to remodify the systems totally.
• Placing the problem that was happening on reality into the system development plan that will be done.
Investigation Tactics
Why do we need tactics?
o To discover all possible problems
o To know the cause of the occuring problems.
o To find the appropriate solution.
Some of the tactics we could perform :
• Listen to the opinion of the systems user, and do not lecture them.
If you know all answers, sure you will not do the investigation. In activity of investigation, we better give enough time for management side or user to explain clearly, and make sure the system analyst doesn't predominating the discussion.
• Don't give the resolving early to problem (do not presolve the problem).
Mean don't try to show the idea to solve problem, before all activity of investigation is completed done.
• Compare solutions from different user.
People mean to have a different point of view to a same problem. So we shall not listen from one source so that there's only one point of view (opinion). When user have difference of view, it;s better to look for his difference and then look for the view that has same equality.
• Observe for a logical inconsistencies.
Logical inconsistencies stops a data flow, where the data could be lost, or suddenly emerged with the selected data. Some matters related to this problems :
o There are data entered but there’re no output (black hole).
o There are output but there’re no inputs (miracles).
• Expect a hard work.
We should be a patient and professional detective in handling problems of system gradually and continually.
• Avoid politics.
System analysts mission is fact not judging.
Investigation Technique
• Direct (Internal) Investigation :
This method is to know directly what is going on in user environment. They permit you to observe directly through it without going through selected sides (interpreter). Internal probes is the source of disruptive, because it may cause an arising in difference of attitude. There are three technique to do the direct investigation, those are:
o Questionnaires
This technique is very precise, if in an investigation has the needed expenses and time constraint. As for things in questionnaire condition of explanation will be difference if we look it directly (face to face interview). The best usefulness from questionnaire is a document was able to show differences that happened at the responder.
o Interview.
This activity required the specialty and time. Everybody couldn’t do the question and answer successfully. Interview question can applicable to a more successive beside it was more flexible as according to field condition.
o Observation.
Observation is a powerful internal investigation. Take a seat with the systems user by doing the perception with a more specific question. Like : why did you do this activity? or where this document will be removed? Every question is possibly can show the mysterious trouble-shooting.
• Indirect (External) Investigation :
This activity can be done swiftly and invisible of personal operational, so with this we can know the external side or something that was hidden from the user community. Ex :
o Procedure flow.
Procedure operational is medium for officer that is newly understand his work and experience of employees to handle the problem. If the flow of aprocedure is not going right, the information system also cannot be operated correctly. Use the systems flowchart to trace the way information as procedure explained in this operation. If there is this problems of procedure, the problem possibly will arise in the operational to be in reality.
o Document review.
By getting and collecting the important document (critical document). If a problem would happened in customer orders, we should collect the original document source from customer orders which used as the entry data, interactive screen format, detail transaction, summary and mistake of report that happened. The document often become the cause of the problem.
o Sampling.
We might require information from vendor billing which have given the discount at the time of payment, because company of discount moment money loss is not given on the happening of delay of payment. You can entangle customers of payer to get the information (despite of many transactions). Finally you can list sample data with election random for the one of last week, choose 20 page of daily transaction, choose 5 item from each chosen page, record the information to each 5 item and count average and variant to samples from all payment transactions that happened.
o Tabular tools
Named also matrix, that is a checklists to find a dismatch in transaction path.
Systems description at this point
Determining the system performance in this time will find it difficult if the company doesn't have a standard measurement of system performance. It’s very unfortunate, that the company tend to not renewing (to update) the system documentation. Therefore, an analyst should improve the document during investigation problem of a system. Descripting system is in this time covers the explanation below :
• Inputs
• Outputs
• Files
• Data elements
• Transaction and action document volume
• Data flow diagrams
Requirement Analysis
Intensive interaction phase between system analysts and end user where the system development team show their skill to get response and trust from the user so that get we can get a good participation from them. Four objectives that should be attained :
- Explaining the systems completely.
- Giving a big picture of how is an ideal information system.
- Bring the ideal information system to this current state with paying attention to the resource constraints.
- Giving a persuasive motivation to the user in developing system.
Requirement Analysis Method
Selection of data collecting method, is required to doing a correction in the requirement system. The methods are interviews, questionnaires, observation, procedure analysis, and document survey. They are :
- Interview
1. How the method is used.
• Select potential interviewees.
• Make an agreement to the potential interviewees.
• Prepare the complete question structure and clearly.
• Choose the person which will be interviewed personally and immediately record it.
2. Goals of the method.
• Personal key in course of DFD.
• Sometimes involve the outsider, like the customers or vendors.
3. Advantage of method.
• Interviewer can measure the respond through question and accommodate it according to the situation that happened.
• Good to the problems that doesn't have structures.
• Show impression to the interviewer personally.
• Peeped out the high response since compilation of meeting.
4. The disadvantage of the method.
• Require dozens of expenses and times.
• Require the special experience and training of interviewer.
• Difficult, compare to the report interview because of subjective natural.
5. When is the method good to be used
• Get the explanation or view from the personal key.
• Test the credibility from interviewees.
• Look for interviews which is contradicted.
• Stabilize the credibility team.
- Questionnaire
1. How the method is used.
• Designed by using standard questionnaire.
• Questionnaire was delivered to the end-users environment work.
• Structure respond summarized in distribution statistic.
2. Goals of the method.
• All end-user with their horizon will be involved in the solution process resolving of system.
• End-User attributed to the process usage of symbols in DFD.
3. Advantage of method.
• Cheap and quick at the interviews.
• Don't require investigator which train only one required expert to design questionnaire to end-user chosen.
• Easy to predict the result of since making questionnaire.
• Easily minimize the expense for all end-user.
4. The disadvantage of the method.
• Cannot make specific question for end-user.
• Cannot show the person end-user.
• Inadaptable of question to end-user specific.
5. When is the method good to be used.
• Simple when asking, and don't have the ambiguous meaning.
• Require wide knowledge from end-user.
• If we only have a few time and expense.
- Observation.
1. How the method is used.
• Personally, an analyst visit the perception location.
• Analysts record the occurrence in perception location, including processing of spread sheet.
2. Goals of the method.
• Process location is geographically shown in DFD (Data Flow Diagram)
3. Advantage of method.
• Get the fact records (data in reality) rather than opinion.
• Don't require question construction.
• Don't disrupt or hide something (end-users don't know that are being perceived).
• Analysts didn't base on the verbal explanation from end-users.
4. The disadvantage of the method.
• If seen, analyst is possibly alter the operation (end-user feel to be perceived).
• On a long term, the fact obtained in one observation might not precise (representative) daily or in a condition weekly.
• Require the experience and special expertise of analyst.
5. When is the method good to be used.
• Require the quantitative picture, as like time, volume, etc.
- Procedure Analysis.
1. How the method is used.
• With this method we can study and identify the document stream lock passing the information system, that is with the data flow diagram (DFD).
• Every key document stream, explain the system operating procedure.
• Through observation, analyst study the reality, than describes the distribution volume (high, lower, medium) and what to do next is to done copying its genuine document.
2. Goals of the method.
• Special document in DFD (Data Flow Diagram)
• Process in DFD.
3. Advantage of method.
• Workable Procedure evaluation with interferences.
• Minimum and not influencing the user operation.
• Stream procedure can become a structure checklist to do the observation.
4. The disadvantage of the method.
• Procedure might not complete and not up-to-date again.
• Studying document stream schema require the time.
5. When is the method good to be used.
• When deciding to do a problem failure of system can assist good scheme.
• Analyst team don't totalize familiar with document stream.
• Describe the document stream disruption activity of function.
- Document survey
1. How the method is used
• Identify the special document and report (physical data flow diagram).
• Collect the real document copy and report.
• Each report or document, used to record data, cover the field ( type and measure), usage frequency and coding structure.
2. Goals of the method.
• Data key stream shown in data flow diagram (DFD).
3. Advantage of method.
• Minimization has been interupted from his operational function.
• Start of data dictionary element.
• Often can consider the fortunate modification procedural.
4. The disadvantage of the method.
• Require more time (there are natural business organization report and document floods).
5. When is the method good to be used.
• Could be used if a system will be designed (during activity of analysis, in clarifying design new system and document analysis can assist to determine the scheme duty hereinafter).
- Sampling
Sampling can assist to lessen the expense and time. We must becareful to choose sample from the population, so that is not experiencing of threat or failure.
Constraint of the Resources
- Time
- Expense
- Expert skill
- Technology
- External factor
Requirement Analysis Document
- Analysis Instruction : Relationship with end user, process monitoring, problems in collecting data
- User Requirement : Real requirement, document requirement, training and new system influence requirement.
- Systems constraint : Explain the time and costs constraint, skill, technology, and external factor.
- Document could be in form of data collection instrument, statistical consensus, logical and physical data stream, initial data element in data dictionary.
Generating Systems Alternatives
How to approach the current state of the system with the ideal system condition :
- By making alternative to solve information system problems.
- Those best alternatives must be applied wisely.
Strategic option :
- Distributed versus centralized processing
Transformation of information decision from centralized data processing to decentralized end user responsibility center.
- Integrated versus dispersed database
Systems developer must consider which data that was entered into the database and into files.
- Surround Strategy of System Development
Sorrounding environment strategy is important in company's take-over because the information system from other company might be different from this current company.
choosing tactics :
- Is done before operational designing selection.
Operational designing selection
Could be grouped into :
- Input
- Online vs Offline Data Entry
- Keyed vs Machine Readable Data Entry
- Centralized vs Decentralized Data Entry
- Processing
- Batch vs Realtime Record Update
- Sequential vs Direct Access To Records
- Single vs Multiple User Update of Records
- Output
- Traditional vs Turn Around Document
- Structured vs Inquiry Based Reports
SELECTING THE PROPER SYSTEM
Comparison strategy : System is compared based on the costs and the profit relatively. There're three ways to say that system A is more superior than other system :
- A has less cost than B, and their profit is equal
- A has less cost than B, and A has more profit than B
- A and B has the same cost, but A has more profit than B
System Comparison Method
- Break Even point Analyisis
- Payback Period
- Discounted PayBack period
- Internal Rate of Return
Costs Category
- Hardware
- Software
- People
- Suppliers
- Telecommunications
- Physical Sites
Costs Spesification
Comparing information system expense through systems life, analysts project how much is the costs conversion for the future and there're three information system costs model, those are the Linear, Eksponensial dan Step Function.
Information system costs may exist just once and might also be continous.
- The information system costs that exist just once is called the ontime cost and the development cost that exist when systems being developed.
- The information system costs that exist continually is called reccuring cost and operational cost where this costs is existed when the information system is on charge daily.
INFORMATION SYSTEM FACTOR
Qualitative factor that was referred to a good information system, are :
- Decreasing the mistake level
- Decreasing the time to correct mistake
- Decreasing the response time from alternative workstation
- Quicken the time to providing information
- Increasing the security level
- Extend the update for active record resources
- Increasing the satisfaction of the user
Company Strategy Factor
- Customer satisfaction
- Selling standard increased
- Customer and vendors commitment
- Product selling information
REPRESENTATING THE SYSTEMS LEARNING
- Doing a brief presentation
- Decreasing the technical explanation in detail
- Presentating clearly with help of visual tools
- If using model, use tools like laptop so that it become more informative
- Emphasize the profit from information system suggestion with existing possible alternative in suit with the condition on the company.
DECISION TO EXTEND OR NOT
- If a company decide to develops the system so then the information department shall do the next process that is System Design Process
- If otherwise, then the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) will be stopped
- Often we will find a problem with the study system and usually the top management shall ask for reprocessing of the study system
- The model will explain some part of the phase that was reprocessed and sometimes the information department will make a decision to repeat the phase before explaining the study system
- With the alternatives, a decision to repeat the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) beforehand or not, is called a Go–No–Go Decision
Minggu, 29 Maret 2009
Minggu, 08 Maret 2009
third quiz - summary of chapter 2
1. What is the importance of developing an information system?
The importance of developing an information system, where in this term means developing a new system, is because the old system needs to be replaced due to the reason :
a. There’re problems that occur in the old system. In example :
1) System’s amiss.
Could be in the form of on purposed fraud or coincedental mistake that makes the inconsistency on the data.
2) Organizational growth.
The necessity to build a new system by organizational growth was because the need of information is going wide, the volume of data processing is increasing, and the changes of new accountant fundamental.
b. To achieve opportunities.
On competing trade, information rate or time efficiency determines the succesive of the strategy that had been planned to achieve the opportunities. So we need to gain advantage of this matter to make the opportunities come to our company, not to the others.
c. The existence of directives.
A new system can be born of superior level order or external organization factor. In example, a government regulation.
2. What is the purpose or goal of developing an information system?
Because of the presence of the problems, opportunities, and the directives, so a new system needs to be developed in order to solve those problems. That is to resolve the problems, to gain the opportunities, and to fill in the directives.
3. What are the organizations expectations after implementing an information system?
On implementing the new system, we expect to gain enhancement in this new system. This new enhancement related to this PIECES :
a. Performance.
Performance can be measured by throughput dan response time. Where throughput means the total amount of work that can be done on one certain time, and response time means an average of delayed time between two transactions or work plus response period to respond that work.
b. Information.
An increasing of information quality.
c. Economy.
An increasing in advantages or benefits or decreasing in cost.
d. Control.
An increasing in control to detect and fix the failure or deception that would happen.
e. Efficiency.
Efficiency here related with how the resource being used with a minimum waste. Efficiency can be measured from output divided with the input.
f. Services.
An increasing of services that was given by the system.
4. What are the principles of developing an information system?
a. The system that was developed is for a managements usage.
Because the one who will use the system is in management level, so the new system must support the requirement of the management level itself.
b. The system that was developed is a big investment asset.
In investing asset, we must consider :
1) All available alternatives must be investigate.
If all other available alternatives were to be ignored and we had invested the fund to certain project, so the investor here had lose the opportunities to invest the fund to other investment. Therefore, from some available investment alternatives, all must be investigated to specify the best alternatives or the most prosperous one.
2) The best investment here must be valuable.
This investment can be said prosperous if it is valuable, which means the benefit or the revenue is bigger than the cost to get them. Where the cost benefit analysis or cost effectiveness analysis can be used to determine whether the investment project is valuable or not.
c. The system that was developed needs educated people.
Peoples that was involved in development as well as in application of the system, must be educated about the problems that exist and educated with solution-solution that it should take. And educated here, doesn’t mean to be a formally colleger, but also can be done with on-the-job-training.
d. Working phase and assignments that have to be done in system development process.
Before doing the system development process, earlier we need to make a working schedule that shows the working phase and assignments that shall be done, so that the system development process could be done and completed succesfully due to the time given and planned budget.
e. System development process mustn’t be in sequence.
Working phase from system development process represents the actions that needs to be done and this actions mustn’t be in sequence, but could be done all together.
f. Don’t be afraid to cancel a project.
For some case where a project must be cancelled because it was not worthy to continue, so the decision must be taken clear. Hesitation to keep going on the project that was unworthy to continue because of the invested funds so far on the project, will just make another waste of the investment itself.
g. Documentation is a must to be the guidance in developing system.
Many system analysts fail to make a documentation. They usually make this documentation after the development of the system or even there’re some that don’t make it. This problem must be revised. So for other system analyst, we suggest to make the documentation all together with the ongoing process of developing system. Because this documentation can be produced from the working output in every steps on system development.
5. System development life cycle.
a. Waterfall Model

This life cycle model take the form of the waterfall, because it goes only one way, like a waterfall that goes only from the top to the bottom. This model also called a sequential model or a sequential linear model. Like what we can see from the upper picture, this model goes one way as sequence from the Requirements phase, to the Design phase, then Implementation phase, Verification phase, and Maintenance phase.
So the process only goes once, as for at the requirements phase we gather all the specification and the requirements of the system, and then we start to make a sketch of design that later will be the systems design at the Design phase, and then implementing all of the planning before like the design, the systems spec and req, and so on. Or on the other hand we executes all the planning here on the Implementation phase. And then at the Verification phase we test all the thing that we have implemented before and make sure that the system runs smoothly and have no problems. After that, we only have one last phase that is Maintenance phase. In this phase, we maintenance the system that means, if there’re any problems regarding the systems, we fix it here. And keep balancing of the process of the systems.
b. Iterative Model

At iterative model, it actually resembles the waterfall model or sequential model. The phases here don’t differ very much. It only different in iterative processes only. This model has a corrective looping phase that is useful to correct failure in the systems. In the picture, it shows on the looping phase between : Planning, Requirements, Analysis & Designs, Implementation, Testing, and Evaluation. These phases show looping condition that means if there’re failure when implementation phase, we need to tests the system again and check where’s the failure going on, and then evaluates them again to be able make a new plan of system, that has a correction of the failure before. If the system has been recreate again and pass the implementation phase, then the system can be deployed (at Deployment phase).
c. Spiral Model
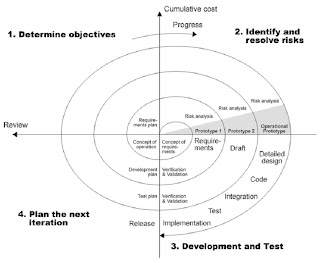
This spiral model at first was proposed by Boehm. Spiral model here is an evolutionary model that joins the two characteristics of iterative model with a control process and systematic aspects from the sequential model. This spiral model splits some activity framework, that also called tasks region, into 6 tasks region. They’re :
1) Customers communication.
Tasks that was needed to develops an effective communication between developer and the customer.
2) Planning.
Tasks that was needed to defined the resources, accurate time, and other related project information.
3) Risk Analysis.
Tasks that was needed to estimate the risks, either in management or technical.
4) Engineering.
Tasks that was needed to build one or more representation of that application.
5) Construction and Deployment.
Tasks that was needed to construct, testing, installing, and giving services to the customer (i.e. training and documentation).
6) Customer Evaluation.
Tasks that was needed to get a feedback reaction from the customer based on software representation evaluation, that was made during engineering phase, and implemented during installation phase.
6. Approaches in system developments.
There’re 5 approaches here. They’re :
a. Classical approach vs Structural approach
Classical approach develops the system with following the phase in systems life cycle. This approach emphasizes system development could be successful if we follow the phase in systems life cycle. But in fact, this approach doesn’t give an advanced guidance about how to do those phase in detailed. So we need a new approach, and so called the structural approach. This approach tries to provide a system analyst with an addition tools and techniques to develops system besides it still follows the idea from system life cycle.
1) Classical Approach.
Classical approach or so called the conventional approach is an approach that follows the phase in systems life cycle without providing itself with adequate tools and techniques. So there goes the problems in this approach, they’re :
a) Developing software has become difficult.
Classical approach gives a minimal tools and techniques in developing a system, and as the consequences the development of software has become aimless and hard to be done by the programmer.
b) The upkeep cost or systems maintenance becomes expensive.
The most expensive cost of system developments is in the maintenance phase. Why the most cost is in it, because the systems documentation is not perfect and not structured. So that when maintenancing system, it has become troubles.
c) Possibility of the system’s making a mistake is high.
Classical approach doesn’t provide the system analyst the procedures to do a test to the system, so that the possibility of the systems to make mistakes is become higher.
d) The success of the systems becomes less guaranteed.
Classical approach didn’t involved the systems user in developing system, so that the needs of the systems user become less suited with what was hoped for before, and as the consequences the applied systems also becomes unsuccessful.
e) Problem in implementing systems.
Because of the less involvement of the systems user in systems development phase, so the systems user will only know the new applied systems in the implementation part only. That will later make the user becomes frustrated because of the lack to operating the system properly.
2) Structural approach.
With only following the phase in system life cycle, wouldn’t make the information system development becomes success. Therefore we need a system development approach to revised them. So there’re this structural approach. This structural approach was equipped with tools and techniques that was needed in developing system, so that we will get a system with a more good and clear structure for the final output.
b. Piecemeal approach vs System approach
Piecemeal approach is a system development approach that emphasizing on an event or certain application only. In this approach, choosen event or application was developed without paying its attention in information system or without paying attention of the global objectives from the organization, but just paying attention on objective of the event or their application only.
But in system approach, we do pay attention for the information system as one unity that was integrated one another for each event or the application. This approach also paying attention on the global objective of the organization, not only the objective of the information system.
c. Bottom-up approach vs Top-down approach
Bottom-up approach, starts from the lowest level of the organization that is on operational level where the transaction happens. This approach starts from formulation of the necessity to handle the transaction and going up to the upper level with formulating the information needs based on that transaction.
On the other hand, the top-down approach starts from the top level organization, that is on the strategic planning level. This approach starts from defining the objectives and policies of the organization. The next step is to do the information needs analysis. After the information needs being defined, so the process goes down one level to the transaction processing, that is to defined the output, input, database, operational procedures and controls.
d. Total-system approach vs Modular approach.
Total-system approach is an approach that develops the system simultaneously in the mass. Differ from the modular approach, where this approach tries to solve a complex system into some part or simple modul, so that the system will be easier to understand and develop.
e. Great loop approach vs Evolutionary approach.
Great loop approach implements a simultaneous change in the mass using advance technology. Differ from the evolutionary approach where it only implements advance technology for the application that need it at that time only and will keep developing for the next period following the necessity of the evolving technology.
7. Please explain the methodology, method, and algorithm.
Methodology is a unity of methods, procedures, working concepts, rules and postulates that was used by certain knowledges, arts or other disciplines. But the method here is a procedure or systematical technique that was used to doing something. And so the system development methodology is a methods, procedures, working concepts, rules and postulates that was used to develops an information system. So then the procedure sequences to solve this problems was known by “algorithm”.
8. Three classification of system development methodology :
a. Functional decomposition methodologies.
This methodology emphasizing in splitting from system into a more small subsystems, so that it will be easier to understand, designed and applicable. The one that includes in this methodology are :
· HIPO (Hierarchy plus Input-Process-Output)
· Stepwise refinement (SR) atau Iterative stepwise refinement (ISR)
· Information-hiding
b. Data-oriented methodologies.
This methodology emphasizing in the characteristics of the data that will be processed. This methodology can be classified into 2 class, those are :
1) Data-flow oriented methodologies.
This methodology was based on the splitting from the system into moduls that was based from the data element types and logic characteristic of that modul in the system. The one that includes in this methodology are :
· SADT (Structured Analysis and Design Techniques)
· Composite design
· Structured Systems Analysis and Design (SSAD)
2) Data-structure oriented methodologies.
This methodology emphasizing in structure from the input and output in the system, where this structure will later be used as a base structure for the systems. The one that includes in this methodology are :
· JSD (Jakson’s systems development)
· W/O (Warnier/Orr)
c. Presciptive methodologies.
The one that includes in this methodology are :
· ISDOS (Information System Design and Optimization System)
ISDOS is a software that was developed in the University of Michigan, where its function is to automated the process of information system development.
· PLEXSYS
The function of PLEXSYS is for transforming a high level language statement into an executable code for a configuration of the desired hardware. PLEXSYS is a complement for ISDOS, where ISDOS was used in determining needs, and PLEXSYS was used in producing the program code automatically.
· PRIDE
PRIDE was offered by a company in America, by M.Bryce & Associates. PRIDE is an integrated software good for designing / analizing system structure, data management, project management and documentation.
· SDM / 70
SDM (System Development Methodology / 70) was developed and sold in the market by a company in America, by Atlantic Software, Inc. SDM / 70 is a software that contains a collection of methods, estimations, documentations and administrative reference to help the user to develops and maintenancing system effectively.
· SPECTRUM
SPECTRUM is a system developmenty methodology that was developed and sold in the market by an American company named SII (Spectrum International Inc.). This software has some version for different needs, like SPECTRUM-1 (for conventional life cycle), SPECTRUM-2 (for structured project management system) and SPECTRUM-3 (for online interactive estimator).
· SRES and SREM
SRES (Software Requirement Engineering System) was developed by TRW for SDS (Software Development System) from US Airforce. In SRES, the user needs was defined in RSL (Requirement Statement Language). And the methodology that was based on this software is called SREM (Software Requirement Engineering Methodology). This software has some identic concepts with ISDOS.
· Some other prescriptive methodologies :
- Chapin’s approach
- DBO (Design By Objective)
- PAD (Program Analysis Diagram)
- HOS (Higher Order Software)
- MSR (Meta Stepwise Refinement)
- PDL (Program Design Language)
9. Tools for Developing Systems are :
- Graphical tools :
a. HIPO Diagram, used in HIPO Methodology and in other methodology.
b. Data Flow Diagram, used in Structured Systems Analysis and Design methodology.
c. Structured Chart, used in Structured Systems Analysis and Design methodology.
d. SADT Diagram, used in SADT methodology.
e. Warnier / Orr Diagram, used in Warnier / Orr methodology.
f. Jakson’s Diagram, used in Jackson System Development methodology.
- Other useful tools are charts, which can be used in almost all other methodologies. These charts are :
a. Charts for explaining activity (Activity Charting) :
1) Systems Flowchart
2) Programs Flowchart, can be in form of :
a) Program Logic Flowchart
b) Detailed Computer Program Flowchart
3) Paperwork Flowchart or Form Flowchart
4) Database Relationship Flowchart
5) Process Flowchart
6) Gantt Chart
b. Charts for explaining layout (Layout Charting)
c. Charts for explaining personal relationship (Personal Relationship Charting) :
1) Working Distribution Chart
2) Organization Chart
10. Techniques used in developing a system :
a. Project Management Technique, that is CPM (Critical Path Method) and PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique). These techniques was used for scheduling project.
b. Fact Finding Techniques, that is a technique to gather data and finding facts in the event to study the existing system. Some of these techniques are :
1) Interview
2) Observation
3) Questionaires
4) Sampling
c. Cost Effectiveness Analysis or Cost benefit Analysis
d. Technique for performing meeting
e. Technique for inspection / walkthrough
11. System Analyst is a person whose job is to analize the system (learn the possible problems that might occur and determine the necessity of the systems user) to identify the reasoned solution possible. The one who understand well about the business aspects of the systems are the systems user itself. So system analyst is the right people to develops information system based on the needs that user wants, while the programmer develops the program application.
The programmer on the contrary with systems user, has more understanding in computer technology, but has less understanding in business aspects and requirement that was needed by systems user. Because of that, we need system analyst to bridge the gap between programmer and systems user. Because he / she, has a great understanding for the two aspects, that is the computer technology aspects to be able to communicate with programmer, and the business aspects to understands what systems user wants.
Knowledge and skills that was needed by most analyst system :
a. Knowledge and skills about data processing technique, computer technology, and computer programming.
- Technical skill that has to be owned includes the skills in using tools and technique for developing application software and skills in using computers.
- Technical knowledge that has to be owned includes the knowledge of computer hardware, data communication technology, computer languages, operation system, utilities and other softwares.
b. Knowledge about business in general.
This knowledge must be owned because nowadays business application is the most application applied. So the knowledge about business is also needed here. This business knowledge includes finance accounting, money accounting, management accounting, management control system, production marketing, personnel management, finance, organization behaviour, company policies, and other business aspects.
c. Knowledge about quantitative method.
Quantitative method that generally needs are : linear programming, dynamic programming, regression, network, decision tree, trend, simulation, and so on.
d. Solving problems skills.
System analyst must have skills to splits complex problems into small subproblems, analyze them, and then unite them again to be a system that can solve the previous problems.
e. Communication skills inter-personnel.
System analysts must have skills to establish communication verbally or in written. These skills was needed in interview, presentation, meeting, and making documentation.
f. Skills to build relationships between personnels.
This skill was needed by system analyst because system analyst need to establish a good relationship between the personnel, in order to avoid a floppy relationships that can cause the job becomes ineffective.
The importance of developing an information system, where in this term means developing a new system, is because the old system needs to be replaced due to the reason :
a. There’re problems that occur in the old system. In example :
1) System’s amiss.
Could be in the form of on purposed fraud or coincedental mistake that makes the inconsistency on the data.
2) Organizational growth.
The necessity to build a new system by organizational growth was because the need of information is going wide, the volume of data processing is increasing, and the changes of new accountant fundamental.
b. To achieve opportunities.
On competing trade, information rate or time efficiency determines the succesive of the strategy that had been planned to achieve the opportunities. So we need to gain advantage of this matter to make the opportunities come to our company, not to the others.
c. The existence of directives.
A new system can be born of superior level order or external organization factor. In example, a government regulation.
2. What is the purpose or goal of developing an information system?
Because of the presence of the problems, opportunities, and the directives, so a new system needs to be developed in order to solve those problems. That is to resolve the problems, to gain the opportunities, and to fill in the directives.
3. What are the organizations expectations after implementing an information system?
On implementing the new system, we expect to gain enhancement in this new system. This new enhancement related to this PIECES :
a. Performance.
Performance can be measured by throughput dan response time. Where throughput means the total amount of work that can be done on one certain time, and response time means an average of delayed time between two transactions or work plus response period to respond that work.
b. Information.
An increasing of information quality.
c. Economy.
An increasing in advantages or benefits or decreasing in cost.
d. Control.
An increasing in control to detect and fix the failure or deception that would happen.
e. Efficiency.
Efficiency here related with how the resource being used with a minimum waste. Efficiency can be measured from output divided with the input.
f. Services.
An increasing of services that was given by the system.
4. What are the principles of developing an information system?
a. The system that was developed is for a managements usage.
Because the one who will use the system is in management level, so the new system must support the requirement of the management level itself.
b. The system that was developed is a big investment asset.
In investing asset, we must consider :
1) All available alternatives must be investigate.
If all other available alternatives were to be ignored and we had invested the fund to certain project, so the investor here had lose the opportunities to invest the fund to other investment. Therefore, from some available investment alternatives, all must be investigated to specify the best alternatives or the most prosperous one.
2) The best investment here must be valuable.
This investment can be said prosperous if it is valuable, which means the benefit or the revenue is bigger than the cost to get them. Where the cost benefit analysis or cost effectiveness analysis can be used to determine whether the investment project is valuable or not.
c. The system that was developed needs educated people.
Peoples that was involved in development as well as in application of the system, must be educated about the problems that exist and educated with solution-solution that it should take. And educated here, doesn’t mean to be a formally colleger, but also can be done with on-the-job-training.
d. Working phase and assignments that have to be done in system development process.
Before doing the system development process, earlier we need to make a working schedule that shows the working phase and assignments that shall be done, so that the system development process could be done and completed succesfully due to the time given and planned budget.
e. System development process mustn’t be in sequence.
Working phase from system development process represents the actions that needs to be done and this actions mustn’t be in sequence, but could be done all together.
f. Don’t be afraid to cancel a project.
For some case where a project must be cancelled because it was not worthy to continue, so the decision must be taken clear. Hesitation to keep going on the project that was unworthy to continue because of the invested funds so far on the project, will just make another waste of the investment itself.
g. Documentation is a must to be the guidance in developing system.
Many system analysts fail to make a documentation. They usually make this documentation after the development of the system or even there’re some that don’t make it. This problem must be revised. So for other system analyst, we suggest to make the documentation all together with the ongoing process of developing system. Because this documentation can be produced from the working output in every steps on system development.
5. System development life cycle.
a. Waterfall Model

This life cycle model take the form of the waterfall, because it goes only one way, like a waterfall that goes only from the top to the bottom. This model also called a sequential model or a sequential linear model. Like what we can see from the upper picture, this model goes one way as sequence from the Requirements phase, to the Design phase, then Implementation phase, Verification phase, and Maintenance phase.
So the process only goes once, as for at the requirements phase we gather all the specification and the requirements of the system, and then we start to make a sketch of design that later will be the systems design at the Design phase, and then implementing all of the planning before like the design, the systems spec and req, and so on. Or on the other hand we executes all the planning here on the Implementation phase. And then at the Verification phase we test all the thing that we have implemented before and make sure that the system runs smoothly and have no problems. After that, we only have one last phase that is Maintenance phase. In this phase, we maintenance the system that means, if there’re any problems regarding the systems, we fix it here. And keep balancing of the process of the systems.
b. Iterative Model

At iterative model, it actually resembles the waterfall model or sequential model. The phases here don’t differ very much. It only different in iterative processes only. This model has a corrective looping phase that is useful to correct failure in the systems. In the picture, it shows on the looping phase between : Planning, Requirements, Analysis & Designs, Implementation, Testing, and Evaluation. These phases show looping condition that means if there’re failure when implementation phase, we need to tests the system again and check where’s the failure going on, and then evaluates them again to be able make a new plan of system, that has a correction of the failure before. If the system has been recreate again and pass the implementation phase, then the system can be deployed (at Deployment phase).
c. Spiral Model

This spiral model at first was proposed by Boehm. Spiral model here is an evolutionary model that joins the two characteristics of iterative model with a control process and systematic aspects from the sequential model. This spiral model splits some activity framework, that also called tasks region, into 6 tasks region. They’re :
1) Customers communication.
Tasks that was needed to develops an effective communication between developer and the customer.
2) Planning.
Tasks that was needed to defined the resources, accurate time, and other related project information.
3) Risk Analysis.
Tasks that was needed to estimate the risks, either in management or technical.
4) Engineering.
Tasks that was needed to build one or more representation of that application.
5) Construction and Deployment.
Tasks that was needed to construct, testing, installing, and giving services to the customer (i.e. training and documentation).
6) Customer Evaluation.
Tasks that was needed to get a feedback reaction from the customer based on software representation evaluation, that was made during engineering phase, and implemented during installation phase.
6. Approaches in system developments.
There’re 5 approaches here. They’re :
a. Classical approach vs Structural approach
Classical approach develops the system with following the phase in systems life cycle. This approach emphasizes system development could be successful if we follow the phase in systems life cycle. But in fact, this approach doesn’t give an advanced guidance about how to do those phase in detailed. So we need a new approach, and so called the structural approach. This approach tries to provide a system analyst with an addition tools and techniques to develops system besides it still follows the idea from system life cycle.
1) Classical Approach.
Classical approach or so called the conventional approach is an approach that follows the phase in systems life cycle without providing itself with adequate tools and techniques. So there goes the problems in this approach, they’re :
a) Developing software has become difficult.
Classical approach gives a minimal tools and techniques in developing a system, and as the consequences the development of software has become aimless and hard to be done by the programmer.
b) The upkeep cost or systems maintenance becomes expensive.
The most expensive cost of system developments is in the maintenance phase. Why the most cost is in it, because the systems documentation is not perfect and not structured. So that when maintenancing system, it has become troubles.
c) Possibility of the system’s making a mistake is high.
Classical approach doesn’t provide the system analyst the procedures to do a test to the system, so that the possibility of the systems to make mistakes is become higher.
d) The success of the systems becomes less guaranteed.
Classical approach didn’t involved the systems user in developing system, so that the needs of the systems user become less suited with what was hoped for before, and as the consequences the applied systems also becomes unsuccessful.
e) Problem in implementing systems.
Because of the less involvement of the systems user in systems development phase, so the systems user will only know the new applied systems in the implementation part only. That will later make the user becomes frustrated because of the lack to operating the system properly.
2) Structural approach.
With only following the phase in system life cycle, wouldn’t make the information system development becomes success. Therefore we need a system development approach to revised them. So there’re this structural approach. This structural approach was equipped with tools and techniques that was needed in developing system, so that we will get a system with a more good and clear structure for the final output.
b. Piecemeal approach vs System approach
Piecemeal approach is a system development approach that emphasizing on an event or certain application only. In this approach, choosen event or application was developed without paying its attention in information system or without paying attention of the global objectives from the organization, but just paying attention on objective of the event or their application only.
But in system approach, we do pay attention for the information system as one unity that was integrated one another for each event or the application. This approach also paying attention on the global objective of the organization, not only the objective of the information system.
c. Bottom-up approach vs Top-down approach
Bottom-up approach, starts from the lowest level of the organization that is on operational level where the transaction happens. This approach starts from formulation of the necessity to handle the transaction and going up to the upper level with formulating the information needs based on that transaction.
On the other hand, the top-down approach starts from the top level organization, that is on the strategic planning level. This approach starts from defining the objectives and policies of the organization. The next step is to do the information needs analysis. After the information needs being defined, so the process goes down one level to the transaction processing, that is to defined the output, input, database, operational procedures and controls.
d. Total-system approach vs Modular approach.
Total-system approach is an approach that develops the system simultaneously in the mass. Differ from the modular approach, where this approach tries to solve a complex system into some part or simple modul, so that the system will be easier to understand and develop.
e. Great loop approach vs Evolutionary approach.
Great loop approach implements a simultaneous change in the mass using advance technology. Differ from the evolutionary approach where it only implements advance technology for the application that need it at that time only and will keep developing for the next period following the necessity of the evolving technology.
7. Please explain the methodology, method, and algorithm.
Methodology is a unity of methods, procedures, working concepts, rules and postulates that was used by certain knowledges, arts or other disciplines. But the method here is a procedure or systematical technique that was used to doing something. And so the system development methodology is a methods, procedures, working concepts, rules and postulates that was used to develops an information system. So then the procedure sequences to solve this problems was known by “algorithm”.
8. Three classification of system development methodology :
a. Functional decomposition methodologies.
This methodology emphasizing in splitting from system into a more small subsystems, so that it will be easier to understand, designed and applicable. The one that includes in this methodology are :
· HIPO (Hierarchy plus Input-Process-Output)
· Stepwise refinement (SR) atau Iterative stepwise refinement (ISR)
· Information-hiding
b. Data-oriented methodologies.
This methodology emphasizing in the characteristics of the data that will be processed. This methodology can be classified into 2 class, those are :
1) Data-flow oriented methodologies.
This methodology was based on the splitting from the system into moduls that was based from the data element types and logic characteristic of that modul in the system. The one that includes in this methodology are :
· SADT (Structured Analysis and Design Techniques)
· Composite design
· Structured Systems Analysis and Design (SSAD)
2) Data-structure oriented methodologies.
This methodology emphasizing in structure from the input and output in the system, where this structure will later be used as a base structure for the systems. The one that includes in this methodology are :
· JSD (Jakson’s systems development)
· W/O (Warnier/Orr)
c. Presciptive methodologies.
The one that includes in this methodology are :
· ISDOS (Information System Design and Optimization System)
ISDOS is a software that was developed in the University of Michigan, where its function is to automated the process of information system development.
· PLEXSYS
The function of PLEXSYS is for transforming a high level language statement into an executable code for a configuration of the desired hardware. PLEXSYS is a complement for ISDOS, where ISDOS was used in determining needs, and PLEXSYS was used in producing the program code automatically.
· PRIDE
PRIDE was offered by a company in America, by M.Bryce & Associates. PRIDE is an integrated software good for designing / analizing system structure, data management, project management and documentation.
· SDM / 70
SDM (System Development Methodology / 70) was developed and sold in the market by a company in America, by Atlantic Software, Inc. SDM / 70 is a software that contains a collection of methods, estimations, documentations and administrative reference to help the user to develops and maintenancing system effectively.
· SPECTRUM
SPECTRUM is a system developmenty methodology that was developed and sold in the market by an American company named SII (Spectrum International Inc.). This software has some version for different needs, like SPECTRUM-1 (for conventional life cycle), SPECTRUM-2 (for structured project management system) and SPECTRUM-3 (for online interactive estimator).
· SRES and SREM
SRES (Software Requirement Engineering System) was developed by TRW for SDS (Software Development System) from US Airforce. In SRES, the user needs was defined in RSL (Requirement Statement Language). And the methodology that was based on this software is called SREM (Software Requirement Engineering Methodology). This software has some identic concepts with ISDOS.
· Some other prescriptive methodologies :
- Chapin’s approach
- DBO (Design By Objective)
- PAD (Program Analysis Diagram)
- HOS (Higher Order Software)
- MSR (Meta Stepwise Refinement)
- PDL (Program Design Language)
9. Tools for Developing Systems are :
- Graphical tools :
a. HIPO Diagram, used in HIPO Methodology and in other methodology.
b. Data Flow Diagram, used in Structured Systems Analysis and Design methodology.
c. Structured Chart, used in Structured Systems Analysis and Design methodology.
d. SADT Diagram, used in SADT methodology.
e. Warnier / Orr Diagram, used in Warnier / Orr methodology.
f. Jakson’s Diagram, used in Jackson System Development methodology.
- Other useful tools are charts, which can be used in almost all other methodologies. These charts are :
a. Charts for explaining activity (Activity Charting) :
1) Systems Flowchart
2) Programs Flowchart, can be in form of :
a) Program Logic Flowchart
b) Detailed Computer Program Flowchart
3) Paperwork Flowchart or Form Flowchart
4) Database Relationship Flowchart
5) Process Flowchart
6) Gantt Chart
b. Charts for explaining layout (Layout Charting)
c. Charts for explaining personal relationship (Personal Relationship Charting) :
1) Working Distribution Chart
2) Organization Chart
10. Techniques used in developing a system :
a. Project Management Technique, that is CPM (Critical Path Method) and PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique). These techniques was used for scheduling project.
b. Fact Finding Techniques, that is a technique to gather data and finding facts in the event to study the existing system. Some of these techniques are :
1) Interview
2) Observation
3) Questionaires
4) Sampling
c. Cost Effectiveness Analysis or Cost benefit Analysis
d. Technique for performing meeting
e. Technique for inspection / walkthrough
11. System Analyst is a person whose job is to analize the system (learn the possible problems that might occur and determine the necessity of the systems user) to identify the reasoned solution possible. The one who understand well about the business aspects of the systems are the systems user itself. So system analyst is the right people to develops information system based on the needs that user wants, while the programmer develops the program application.
The programmer on the contrary with systems user, has more understanding in computer technology, but has less understanding in business aspects and requirement that was needed by systems user. Because of that, we need system analyst to bridge the gap between programmer and systems user. Because he / she, has a great understanding for the two aspects, that is the computer technology aspects to be able to communicate with programmer, and the business aspects to understands what systems user wants.
Knowledge and skills that was needed by most analyst system :
a. Knowledge and skills about data processing technique, computer technology, and computer programming.
- Technical skill that has to be owned includes the skills in using tools and technique for developing application software and skills in using computers.
- Technical knowledge that has to be owned includes the knowledge of computer hardware, data communication technology, computer languages, operation system, utilities and other softwares.
b. Knowledge about business in general.
This knowledge must be owned because nowadays business application is the most application applied. So the knowledge about business is also needed here. This business knowledge includes finance accounting, money accounting, management accounting, management control system, production marketing, personnel management, finance, organization behaviour, company policies, and other business aspects.
c. Knowledge about quantitative method.
Quantitative method that generally needs are : linear programming, dynamic programming, regression, network, decision tree, trend, simulation, and so on.
d. Solving problems skills.
System analyst must have skills to splits complex problems into small subproblems, analyze them, and then unite them again to be a system that can solve the previous problems.
e. Communication skills inter-personnel.
System analysts must have skills to establish communication verbally or in written. These skills was needed in interview, presentation, meeting, and making documentation.
f. Skills to build relationships between personnels.
This skill was needed by system analyst because system analyst need to establish a good relationship between the personnel, in order to avoid a floppy relationships that can cause the job becomes ineffective.
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)
